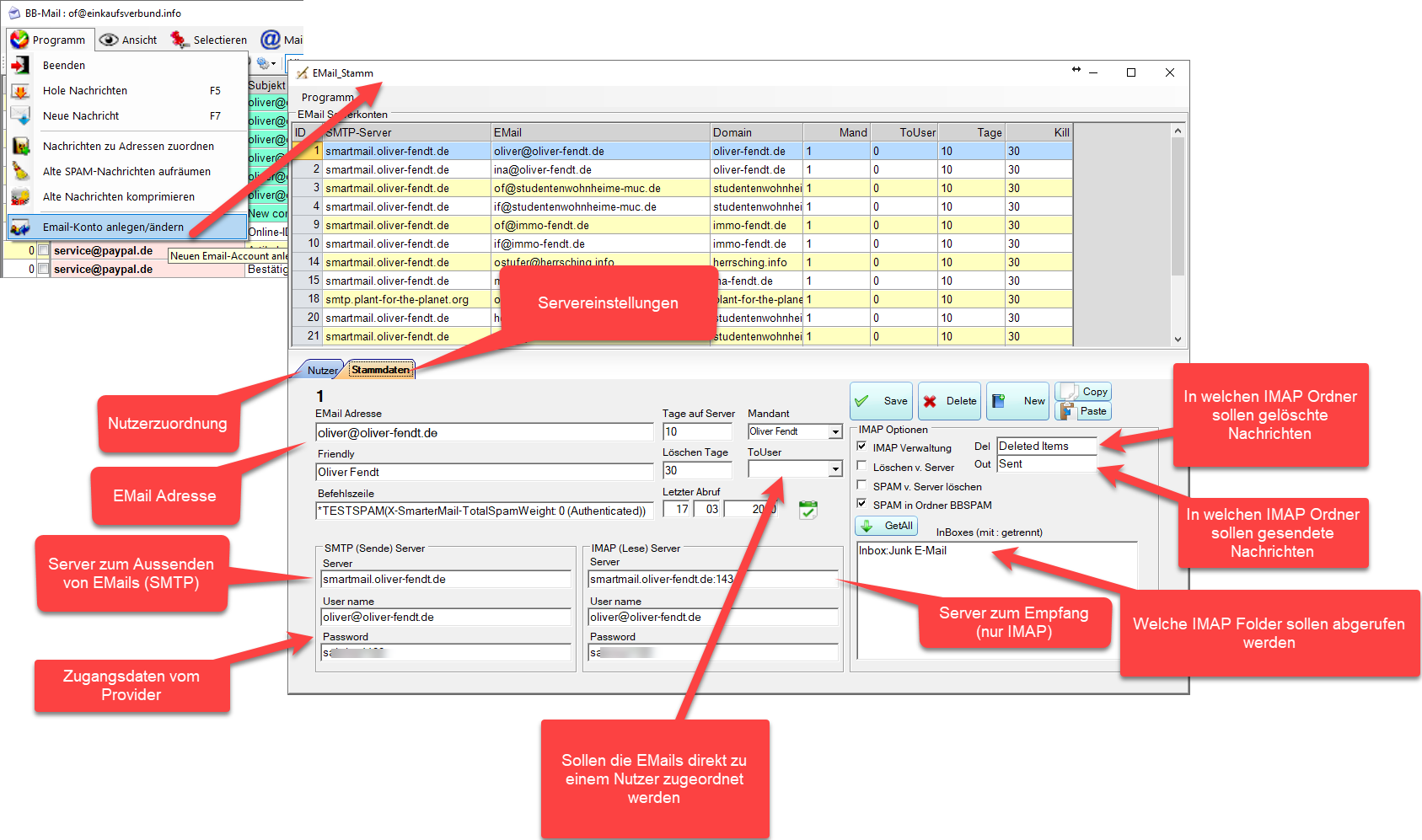
Einstellen des Ports bei SMTP
Wie in der Branche üblich kann der Port mit Doppelpunkt getrennt angegeben werden zB smtp.1und1.de:465
Alternativ kann für einen SMTP-Host auch eine Einstellung in der Config Tabelle vorgenommen werden:
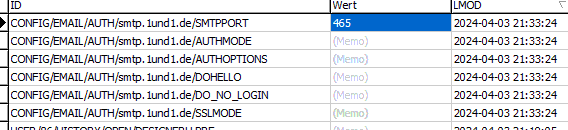
Die Einstellungen für AuthMode:
| Example Title |
Copy Code |
|---|---|
// // Zusammenfassung: // No authentication. Sometimes used with MailBee.SmtpMail.Smtp when the server // allows relay for anonymous senders. None = 0, // // Zusammenfassung: // Standard authentication. Passwords are transmitted as clear-text. Not supported // by SMTP servers. Regular = 1, // // Zusammenfassung: // Secure APOP authentication. Supported by many POP3 servers but cannot be used // with other servers like SMTP because APOP is POP3-specific. Disabled when MailBee.Global.FipsMode // is enabled. Apop = 2, // // Zusammenfassung: // A custom SASL authentication method implemented by the developer. SaslUserDefined = 4, // // Zusammenfassung: // SASL LOGIN authentication. Not secure but widely supported. Passwords are transmitted // as Base64 strings. Note for IMAP users: this is AUTHENTICATE LOGIN command, not // just LOGIN command (which corresponds to MailBee.AuthenticationMethods.Regular // method). SaslLogin = 8, // // Zusammenfassung: // SASL PLAIN authentication. Not secure but widely supported. Passwords are transmitted // as Base64 strings. SaslPlain = 0x10, // // Zusammenfassung: // Secure SASL CRAM-MD5 authentication. Might not be supported by particular server // implementations. Disabled when MailBee.Global.FipsMode is enabled. SaslCramMD5 = 0x20, // // Zusammenfassung: // Secure SASL DIGEST-MD5 authentication. Might not be supported by particular server // implementations. Disabled when MailBee.Global.FipsMode is enabled. SaslDigestMD5 = 0x40, // // Zusammenfassung: // Secure SASL NTLM authentication (also known as Secure Password Authentication // - SPA). In Windows domain environment such as Active Directory, can also be used // to authenticate the current Windows user (in this case, the developer should // pass a null reference (Nothing in Visual Basic) as accountName and password values). // Might not be supported by particular server implementations. May not work in // UWP apps, consider GSSAPI instead. See remarks section for futher details regarding // Integrated Windows Authentication. SaslNtlm = 0x80, // // Zusammenfassung: // Secure SASL MSN authentication (equivalent to NTLM). Not widely supported nowadays. SaslMsn = 0x100, // // Zusammenfassung: // Secure SASL GSSAPI authentication (through Kerberos or NTLM). Like MailBee.AuthenticationMethods.SaslNtlm, // supports Integrated Windows Authentication mode. The internal implementation // (Kerberos or NTLM) is selected upon whether targetName of Login method is an // empty string or not (for SMTP case, MailBee.SmtpMail.SmtpServer.TargetName). // Empty string denotes NTLM, all other values (including a null reference) denote // Kerberos. Also, the underlying implementation downgrades to NTLM from Kerberos // if targetName is not empty but not valid (denotes non-existent SPN). SaslGssApi = 0x200, // // Zusammenfassung: // OAuth v1.0 authentication (widely used by Google in the past). It's a password-only // authentication. To create a key to be supplied as the OAuth password, use MailBee.OAuth // class. As the OAuth account name, specify a null reference (Nothing in Visual // Basic). Note that if you supplied both the password and the account name when // logging in, MailBee will exclude OAuth from the set of authentication methods // to be tried unless MailBee.AuthenticationMethods.SaslOAuth is the only method // listed in this set. This is because OAuth is not compatible with other authentication // methods which require a login and a password, not a "key". You can, however, // specify non-null account name if you explicitly specified MailBee.AuthenticationMethods.SaslOAuth // method to be used for login. This account name can be any string, it won't be // used during the login process itself (because it uses only the password) but // it will be displayed in the log file in place of the account name. SaslOAuth = 0x400, // // Zusammenfassung: // OAuth v2.0 authentication. A newer and recommended version of OAuth. All MailBee-specific // details (listed above in MailBee.AuthenticationMethods.SaslOAuth description) // are valid for this method as well. SaslOAuth2 = 0x800, // // Zusammenfassung: // Tells MailBee to automatically select the best supported authentication method // and downgrade to insecure methods if secure methods are not supported by the // server. This behavior can be changed with MailBee.AuthenticationOptions flags. Auto = 0xFFF Type your Expandable text content here. | |
public enum SslStartupMode
{
//
// Zusammenfassung:
// The developer must manually call StartTls method of the mailer component to switch
// the connection into TLS/SSL mode. However, MailBee.Global.AutodetectPortAndSslMode
// property may cause MailBee to automatically enable TLS/SSL for some well-known
// hosts or ports even if MailBee.Security.SslStartupMode.Manual mode is selected.
Manual,
//
// Zusammenfassung:
// The entire conversation with the mail server will take place under TLS/SSL layer.
// To use this mode, the developer should connect to the mail server on dedicated
// TLS/SSL port (usually, 465 for SMTP, 995 for POP3, and 993 for IMAP4).
OnConnect,
//
// Zusammenfassung:
// The mailer component will automatically call StartTls method when appropriate
// (prior to login for POP3/IMAP4, prior to hello for SMTP). No dedicated SSL/TLS
// port is required (the connection should be made to the regular SMTP, POP3, or
// IMAP4 port). Also, some SMTP servers use the special port 587 for StartTLS -
// the client MUST switch the connection into secure mode using StartTLS after establishing
// the connection to port 587. This is different from connecting to port 25 where
// the client MAY switch the connection into secure mode (it's up to the client
// to decide). StartTLS approach provides the same security level as MailBee.Security.SslStartupMode.OnConnect.
// However, the mail server must support STARTTLS (STLS for POP3) extension.
UseStartTls,
//
// Zusammenfassung:
// Similar to MailBee.Security.SslStartupMode.UseStartTls but does not require the
// server support STARTTLS. If the server supports STARTTLS, MailBee will use it.
// If STARTTLS is not supported, MailBee will not issue this command and the entire
// session will not be SSL-encrypted.
UseStartTlsIfSupported
}
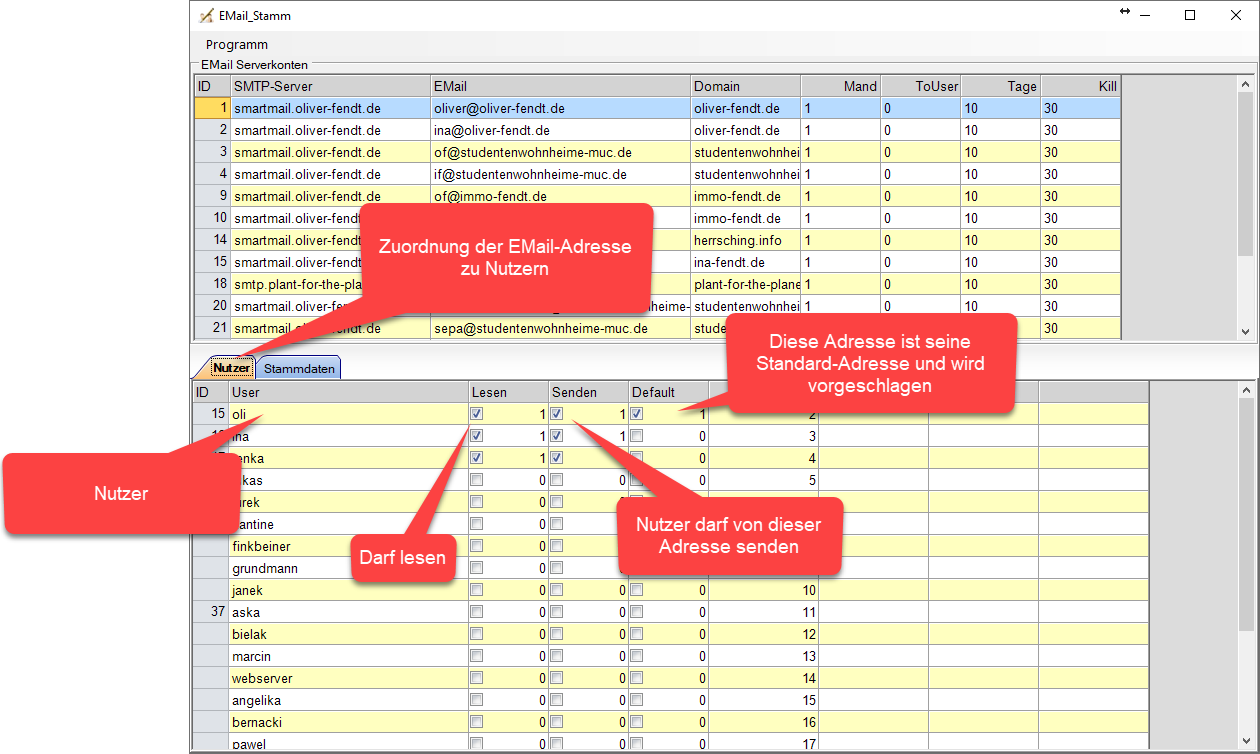
Zugriffsrechte auf EMail-Adressen
Type your Expandable text content here.